Troubleshooting Common SD-WAN Issues
Using the SD-WAN network to connect your data center can be a valuable business tool and you can gain the top benefits of SD-WAN, but there are also specific SD-WAN issues that you need to be aware of. One of these is high CPU usage, leading to high packet loss and other common problems.
High CPU usage leads to high packet loss
Table of Contents
In the SD-WAN world, high CPU usage can lead to poor performance. There are several reasons for this.
One is the fact that the device may be overloaded. This can occur with many applications, including VoIP, telepresence, and mission-critical VoIP. DoS attacks, a significant bandwidth consumption source, can also cause it.
If the system is overloaded, it can cause problems with service and application performance. For example, a 2% packet loss can result in a noticeable reduction in quality. Depending on the actual situation, the outcome may be positive or negative.
Another possible cause of high CPU usage is excessive DHCP or ARP traffic. These activities can result in packet loss.
Another potential culprit is software-based routing, where packets are sent to the CPU instead of processed in hardware. Moreover, there are a large number of online services that can overload a device.
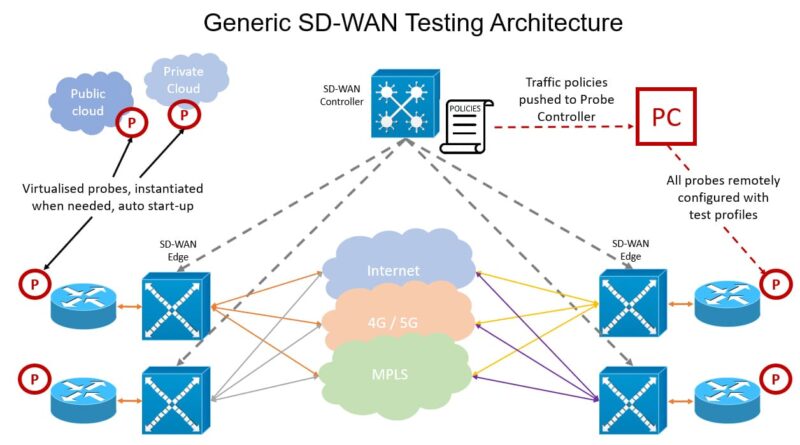
The SD-WAN controller should be able to detect several things to help identify these factors. These include flapping links, interface errors, and duplex mismatches. Moreover, it should be able to alert when physical links are not functioning correctly.
SD-WAN software must be able to work on multiple platforms
SD-WAN software should work on multiple platforms and offer a secure end-to-end network. It should also ensure network agility, resiliency, and performance. Moreover, it should offer flexible network security and support for Quality of Service.
A successful SD-WAN solution’s ability to provide secure and quality traffic management is one important characteristic. Whether it’s on-site data centers or the cloud, SD-WAN can identify and route traffic according to pre-defined rules.
The centralized management plan reduces complexity, minimizes labor costs, and routes traffic efficiently to trusted providers. In addition, SD-WAN offers self-healing capabilities, which improve application performance and user experience.
For example, traffic can easily be directed to another link if a connection fails. Also, if an application needs to be restarted, SD-WAN can automatically re-connect it.
SD-WAN uses a central management controller, which monitors and controls all traffic on the network. It’s also responsible for enforcing policies and providing alerts.
An SD-WAN architecture should be based on cloud-edge services. This allows for flexible deployment options and simplified administration. Additionally, the Edge includes resilience, security features, and online traffic engineering.
SD-WAN encourages the use of multiple links with multiple carriers
You have faced a few common problems when running an SD-WAN network. It is essential to understand what they are so you can troubleshoot them quickly and effectively. For example, if you have a poor branch connection, there are several potential causes. Your local area network, internet links, and the network itself may be involved.
One of the most impressive capabilities of an SD-WAN is the ability to prioritize traffic for higher-priority applications. The system can also be used to deprioritize less important applications.
Another important use of an SD-WAN is monitoring how the network performs. You can use an SD-WAN to detect problems in your branch, including flapping and duplex mismatches. Also, you can use it to monitor your application performance, such as pings, file transfers, and database synchronization.
An SD-WAN needs to be supported by a robust software suite to be effective. This is because it can be difficult to implement and troubleshoot without one. The software gives you the ability to manage traffic more efficiently, and it also provides better data security.
SD-WAN encourages the use of unified threat management
While SD-WANs provide a wide variety of benefits, the technology does carry a few disadvantages. The first is that SD-WANs require proper management. If the SD-WAN isn’t being managed properly, it’s likely that issues will be missed and may even cause problems.
This is especially true when multiple WAN links are used. Since each link isn’t interoperable, troubleshooting can be a real challenge. It’s essential to understand the best ways to measure and evaluate performance.
One of the best ways to do this is to monitor SD-WAN’s topology. An SD-WAN controller should detect packet drops, interface errors, and duplex mismatches. Moreover, the controller should be able to notify users when physical links are failing.
Another way to identify performance issues is to measure how well the SD-WAN network routes traffic. This is particularly important if the traffic is being routed around a broken circuit.
Monitoring becomes more critical as IoT devices expand and enterprise mobility programs grow. In addition to measuring how well the SD-WAN is working, you need to check for issues that could affect the user experience.

SD-WAN encourages the use of visualizations to help troubleshoot and adjust policy
SD-WAN is a form of internet connection that abstracts multiple network links into one. This creates a more flexible framework for ongoing analysis and troubleshooting. It can also improve business performance and collaboration.
The key to a successful deployment of an SD-WAN is to use a modern network performance solution to ensure the delivery of optimal performance to applications. Such a solution can ensure service delivery, maximize visibility, and provide a high-performance user experience.
Traditionally, networks have been based on physical routers and control planes. These routers connect users to applications hosted in data centers. However, today’s businesses may operate in many different geographic locations. In addition, cloud applications are constantly changing. Thus, it is important to have a unified view of the traffic path of the applications.
A basic SD-WAN solution steers traffic according to pre-defined rules. Network engineers write these rules. Depending on the application, these rules may be implemented on a device-by-device basis or in a more centrally configured manner.
To improve troubleshooting, network administrators should use detailed path analytics. This information will allow them to verify that their policy changes are effective. They can also identify internal network problems and ISP or application provider issues.